
Knee pain affects people of all ages and has many causes. It may happen due to medical issues, strains, and overuse. Osteoarthritis is the main type of arthritis that causes knee pain; it is the most common type of knee pain for Kingwood, TX residents in people over the age of 50.
Surgery is not always needed to treat knee pain. Many non-surgical methods can reduce pain and improve the knee's function. These methods aim to fight the causes of knee pain, like inflammation, injured tissues and damaged cartilage.
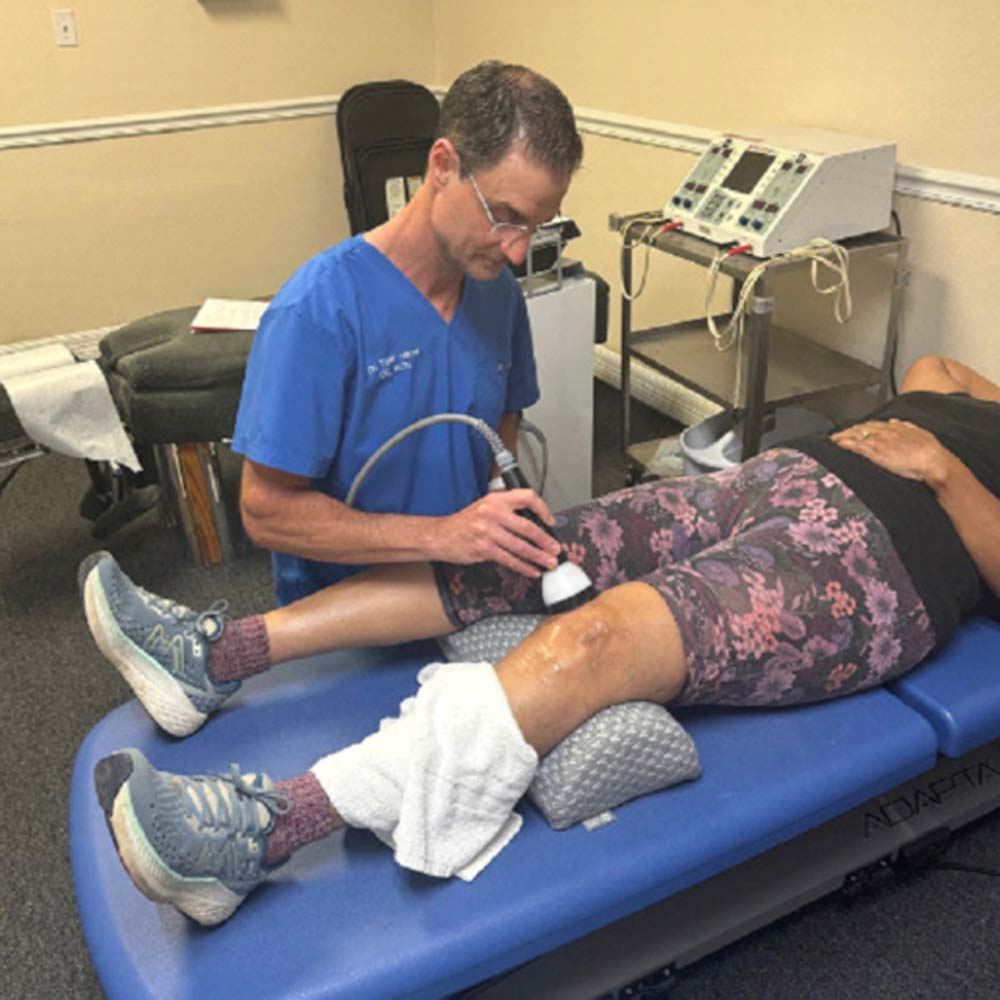
Shockwave therapy is one of the newest, non-invasive, cutting-edge knee pain treatments out there that uses powerful sound waves to reduce inflammation, improve circulation and actually recruits local stem cells to accelerate the healing process.
Taking anti-inflammatories can be one of the keys in treating knee pain without surgery. These drugs lessen pain and swelling from knee osteoarthritis. You can take them by mouth or put them on the skin, based on what works for you. If you are interested in the more natural side of anti-inflammatory supplements, turmeric, glucosamine and fish oil are really good choices.
Braces and orthotics are also helpful in managing knee pain without surgery. They give the knee joint support, easing stress and strain. This is great for people with knee issues or an unstable knee.
Exercising without putting too much stress on your knees is a big plus. Things like swimming, cycling, and yoga make your knee muscles stronger. This helps the knee move better and reduces pain.
Getting injections can help too. One kind, corticosteroids, can lower inflammation for a while. Platelet-rich plasma injections encourage your body's healing and help grow new tissue.
Changing your lifestyle is useful for non-surgical knee pain care. Keeping a healthy weight is important to lessen knee joint strain. Eating foods that fight inflammation also eases pain and keeps your joints healthy.
Physical therapy is a key part of the non-surgical approach. A therapist will create exercises to make your knee stronger and more flexible. They also teach you about right movement to avoid hurting yourself further.
Key Takeaways:
- Osteoarthritis can lead to knee pain, but there are many non-surgical ways to manage it.
- Non-surgical methods include drugs, braces, gentle exercise, shots, lifestyle changes, and therapy.
- Anti-inflammatories can lessen pain and swelling in the knee.
- Braces and orthotics add support and decrease knee stress.
- Low-impact exercises strengthen knee muscles and boost stability.
Leading Causes of Knee Pain
Knee pain has many causes, leading to discomfort and less movement. It's key to know what's causing the pain for good non-surgical care. The main reasons for knee pain are:
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a common knee problem, where the protective cartilage breaks down. This leads to pain, stiffness, and swelling in the knee. At this point in time, over 14% of all American over the age of 50 have some kind of arthritis, it is really common especially in active people.
Strains and Sprains
Activities like sports or accidents can cause strains and sprains. The muscles, tendons, and ligaments around the knee get stretched or torn. These accidents or sudden movements hurt the knee a lot and cause wear and tear of the joint, meniscus and tendons around the knee.
Overuse Injuries
Overusing the knee by doing the same motions again and again can hurt it. The most common repetitive overuse actions are running, jumping, bending, squatting, and twisting. We see a lot of knee injuries says Dr. Hamel in sports like football, pickleball, long distance runners, cross-fit athletes, and basketball players. These sports causes swelling and pain in the knee over time.
Finding out what's causing your knee pain is very important. This helps doctors choose the best way to treat it, without surgery. They can decide based on if it's from arthritis, strains, or too much use on the knee. Most doctors will do a series of imaging including X-ray and MRI to see exactly what is going on with the knee, cartilage and osteoarthritis.

By finding the source of your knee pain, you can get better and avoid surgery. Next, we'll see the choices for treating knee pain without surgery.
Non-Surgical Knee Pain Treatment Options
Dealing with knee pain without surgery has several options. These non-surgical treatments help ease pain and accelerate healing of the knee. They offer ways to avoid surgery while keeping your knee joint healthy.
Anti-inflammatories
Anti-inflammatories help with knee pain. They lessen pain and swelling in the knee. You can get these drugs with a prescription or over-the-counter. Keep in mind that taking NSAIDS over a long period of time can have some negative effects such as wear and tear on the stomach lining, the liver and the kidney.
Braces and Orthotics
Braces and orthotics also help manage knee pain. They reduce stress on the knee and offer support. They make it easier to move by properly aligning the joint and keeping the area warm.
Low-Impact Exercise
Low-impact exercises are vital for knee health. Things like water therapy, pilates and yoga build up muscles without hurting the knee. The knee will always be healthier when it is able t move; this creates a certain amount of blood flow and nerve flow in to the area.
Injections and Infusions
Injections are another way to treat knee pain without surgery. Corticosteroids reduce pain by easing inflammation. PRP injections help the knee heal naturally, which is good for some people. Dr. Hamel says that he has some patients that come in and had great success with cortisone shots and PRP shots while other say they only experienced temporary relief.
Lifestyle Changes
Changing your lifestyle can greatly reduce knee pain. If you lose weight, less pressure goes on your knee. Eating an anti-inflammatory diet also helps. This diet includes good sources of protein, (100-150 grams a day), veggies, and foods high in omega-3 fats.
These non-surgical treatments are great for knee pain, arthritis and other degenerative conditions of the knee. But, it's always best to talk with a doctor. They can figure out what treatments are best for you, depending on the cause and how severe the pain is.
Can Non-Surgical Treatments Postpone Knee Surgery?
Non-surgical treatments can sometimes put off the need for knee surgery. Studies show people with severe knee arthritis can wait about two years before needing surgery. Or, they might not need surgery at all. These treatments include exercises, physical therapy, shockwave therapy, chiropractic, acupuncture, massage PRP injections.
These ways have worked well for some in lessening knee pain and making the joint work better. Mixing different therapies for each person's needs can help. Patients might escape the dangers and months of healing after surgery. But, how well these non-surgical ways work can differ based on how bad the arthritis is for each person and their medical history.
Talking over the risks, pluses, and options with a doctor is very important to decide wisely. A doctor can suggest what's best for the patient's situation depending on how active they are and what their future goals are. This could help the patient avoid or put off surgery while keeping their arthritis in check. Some of our patients, says Dr. Hamel, just want to get out of pain and have a more sedentary lifestyle, but the majority of our new patients want to get rid of their knee pain so they can get back to playing with their kids, traveling, hiking, playing pickleball, going to the gym or golfing; not being active is not an option for them.
The choice to get knee surgery is very personal, and a doctor should help make it. Non-surgical steps might help delay or totally avoid surgery. But, their success should be looked at depending on the individual patient.
Benefits of Non-Surgical Treatments for Knee Pain:
- Delay or avoidance of knee surgery, orthoscopic or knee replacement
- Less risks and quicker recovery than surgery
- Better joint movement
- A better life quality, get back to enjoying gardening or golf
- Specific treatment for each person

Conclusion
People can manage knee pain without needing surgery. They can choose from many non-surgical treatments. These non-invasive therapies help deal with the underlying cause of knee pain. This includes problems like osteoarthritis, patellar tendinitis, bone on bone knee pain, strains, and overuse injuries. Non-surgical treatments also help knee pain by stimulating the body to heal and repair from the inside.
You can use anti-inflammatories to ease the pain and swelling. Braces, orthotics and compression garments give extra support. They help lessen the strain on the knee when you move. Doing exercises like aquatic therapy and yoga are also great, as long as the movements are not irritating the knee pain. The right exercises and stretches make the knee's surrounding muscles strong and joint flexible.
Some treatments involve getting shots in the knee. These can be corticosteroid shots or platelet-rich plasma shots. They can target the pain and lower the swelling. Changing your lifestyle might help too. Losing weight and eating foods that reduce inflammation can better your knee's health. The lower the overall inflammation in the body says Dr. Hamel, the better.
Non-surgical therapies can delay or prevent the need for surgery, however, the right treatment varies for each person. It's key to talk to a doctor. They will help you find the best plan. With this, you could help the pain, improve life quality, and maybe skip surgery altogether. Communication with your doctor is important; let them know your expectations after you do physical therapy, acupuncture, shockwave therapy, chiropractic or a knee scope, depending on what your goals are determines the type and length of treatment you may need.
FAQ
What are the leading causes of knee pain?
Many things can lead to knee pain. These include conditions like osteoarthritis. Also, strains, sprains, and overuse injuries can bring it on. Joint wear and tear can happen with most people and their knees overtime. One of the most common conditions for Americans is osteoarthritis of the knees, especially after age 50. Human being are active, and doing activities like sports, twisting, turning, lifting and certain trade professions can really put stress and pressure on the knee joints, meniscus, cartilage and ligaments of the knee.
What non-surgical treatment options are available for knee pain?
There are several non-surgical options to treat knee pain. Some include using anti-inflammatories, wearing braces and physical medicine therapies. Also, doing corrective exercises that help stabilize and strengthen the knee can really make a difference. Getting cortisone shots/PRP shots can help by reducing inflammation and stimulating healing. Lifestyle changes, losing weight, eating healthy and taking supplements to reduce inflammation always helps the body to be able to heal more efficiently.
Can non-surgical treatments prevent or postpone knee surgery?
Yes, studies show non-surgical options can delay or prevent knee surgery. This is especially true for people with very advanced knee arthritis. In his office Dr. Hamel promotes non-surgical knee treatments using shockwave therapy, chiropractic care, nutritional support and corrective exercises. Many of Dr. Hamel knee pain patients come in because they want to get back to pain free hobbies, gardening, traveling, playing with their kids and sports without having to entertain the thought of orthoscopic surgery or knee replacement.
How effective are non-surgical treatments for knee pain?
The success of non-surgical care can vary. For each person, it depends on their unique situation. Talking to a doctor is important. They can help weigh the pros and cons and then you can make a choice that's right for you. The number of non-surgical treatments has increased over time so it may be well worth it for you to try corrective exercise therapy, nutritional therapy, PRP injections, massage, acupuncture, chiropractic adjustments, physical therapy or shockwave therapy.
What is the role of shockwave therapy in treating knee pain?
Shockwave therapy is very unique in its process, it produces a spark in water and from there an acoustic soundwave, this soundwave penetrates deep into the injured area, the joint, the muscles, ligaments, tendons and cartilage. This wave brings in more circulation and actually agitates the area helping to flush out some of the inflammation. As a bonus, shockwave therapy also recruits local stem cells in the area of injury to help accelerate healing and repair.

